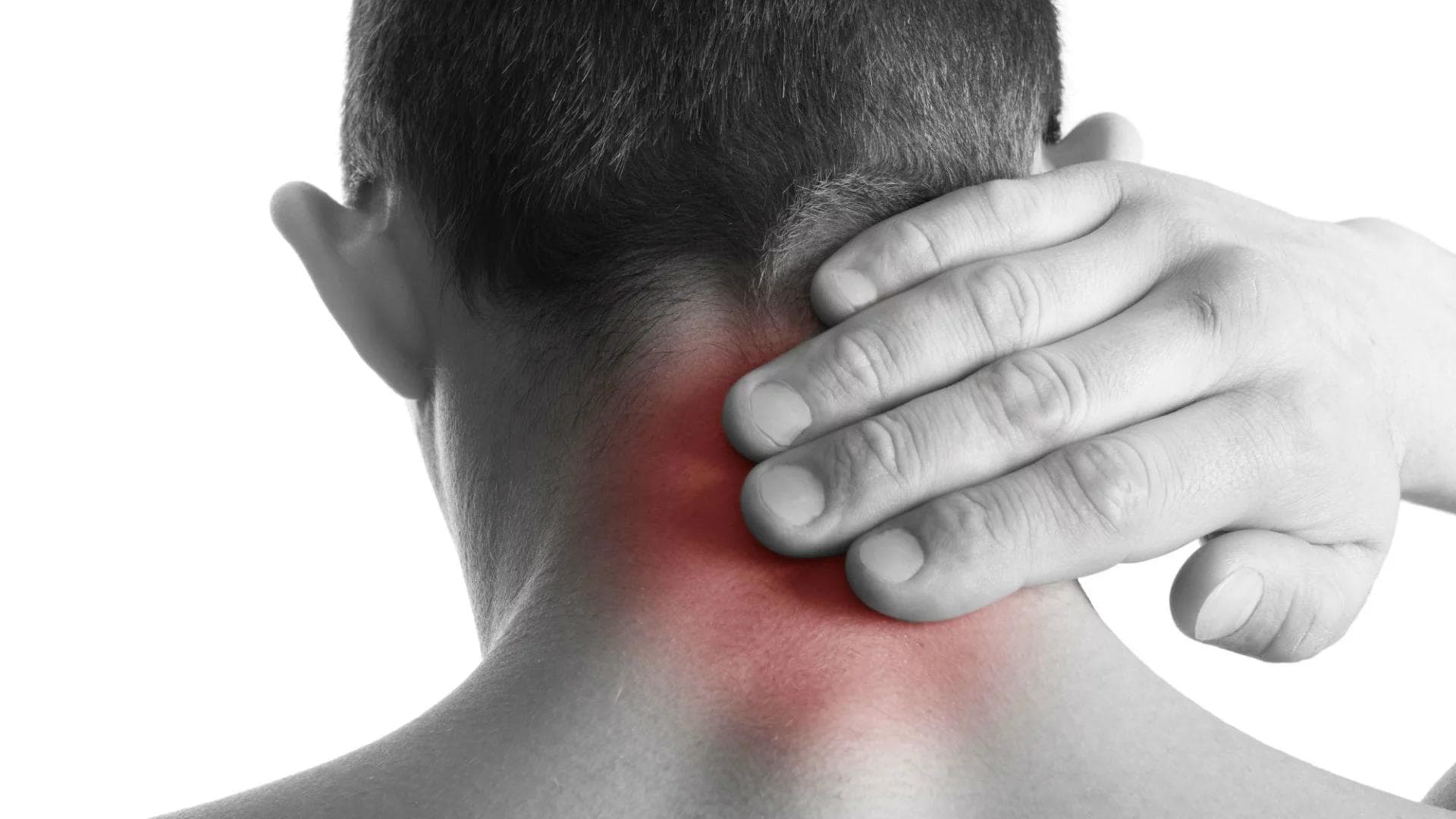
Types of Pain after a Car Accident: Acute vs. Chronic Pain
Free ConsultationThe human body is not designed to sustain the impact of a car accident. Even a minor fender bender can leave victims in pain for days, weeks, or even months.
Unfortunately, car accidents can cause many different types of injuries and pain. Below, our legal team at the PARRIS Law Firm will discuss the definition, causes, and treatments for acute vs. chronic pain after a car accident, as well as what your pain means for your car accident injury claim.
Acute Pain
In the medical world, an “acute” condition refers to one that is sudden and severe in onset. Acute pain, therefore, refers to any sudden and sharp pain that lasts less than six months.
Most acute pain conditions have a clear source, such as tissue damage or a broken bone. Treating the pain usually involves treating the underlying condition.
Causes of Acute Pain after a Car Accident
Several types of injuries can cause acute pain after a car accident, including:
- Cuts and scrapes
- Sprains, strains, and bruises
- Whiplash
- Herniated spinal discs
- Broken bones
- Burns
- Spinal cord injuries
- Traumatic brain injuries, including concussions
Learn more details about these common injuries after a car accident.
Some Pain after a Car Accident is Delayed
When you are in a car accident, your fight or flight response kicks in, pumping adrenaline throughout your body. Adrenaline decreases your ability to feel pain while the response is active, so you may not realize you are injured until hours or days after your initial accident.
After this response wears off and you begin to relax again, your body may alert you to your injuries by swelling and pain at the injury site. However, this may not happen for days, weeks, or even months after the accident.
For this reason, the attorneys at PARRIS Law Firm recommend visiting a medical provider after a car accident, even if you don’t think you are injured. A doctor will be able to diagnose any injuries you may have sustained and treat any symptoms that arise.
Along with seeking medical treatment, speaking to a lawyer may be the best way to protect your rights after an accident. A trusted attorney will ensure that the compensation you receive is enough to cover the cost of your care, even if the onset of your injuries was delayed.
Chronic Pain after a Car Accident
Unlike acute pain, chronic pain lasts more than six months. Roughly 20% of Americans experience chronic pain in some form, but the condition is extremely difficult to diagnose.
Chronic pain is usually triggered by a traumatic event, such as a car accident. Oftentimes, the victim may experience acute pain from their car accident injuries that does not go away as the injuries heal. This condition is what some doctors refer to as chronic pain syndrome (CPS).
Types of Chronic Pain Syndrome after a Car Accident
Chronic pain syndrome (CPS) can show up in many forms, and it is different for each person. Examples of chronic pain include:
- Headaches
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Nerve pain
- Arthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
Though doctors can often identify what triggers chronic pain syndrome, it can be difficult to determine why some people experience lingering pain while others do not. According to WebMD, some doctors think that CPS patients feel pain differently due to differences in their body’s stress response.
Regardless of the cause, CPS can be debilitating for those who experience it. Chronic pain can lead to sleep problems, chronic fatigue, anxiety, depression, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Chronic pain after a car accident can also manifest as other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS).
Acute Pain After A Car Accident Can Develop Into A Chronic Pain Condition.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a condition that causes widespread pain in the muscles and bones. In addition to chronic pain, fibromyalgia can cause fatigue, sleep problems, mood issues, brain fog, and increased pain sensitivity. Unfortunately, this chronic pain disorder often accompanies other medical problems, such as migraines, arthritis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), bladder problems, and anxiety or depression.
Many medical sources cite car accidents as a common cause of the illness.
Doctors also think that genetics may play a role in causing fibromyalgia, as the disorder tends to run in families. In addition, people with autoimmune disorders such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis are also at increased risk of developing fibromyalgia.
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), formerly known as Reflexive Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD), is another specialized chronic pain condition that usually affects the arms or legs. The disorder usually appears after an injury, illness, or traumatic event and presents as pain far out of proportion with the original injury.
MayoClinic lists several symptoms that may indicate CRPS, including:
- Intense, throbbing pain in an arm, leg, hand, or foot
- Extreme sensitivity to touch in the affected limb
- Temperature and touch sensitivity
- Temperature changes in the affected area
- Changes in skin color or texture
- Changes in hair and nail growth in the affected area
- Joint stiffness
- Limited mobility of the affected area
There are two types of CRPS:
- Type 1, which is diagnosed when the patient has no history of nerve damage; and
- Type 2, which occurs after a nerve injury.
Resources for sufferers of CRPS are available at the Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome Association’s website.
Treating Chronic Pain after a Car Accident
The treatments for chronic pain conditions are limited. Oftentimes, chronic pain conditions can’t be “cured,” but symptoms can be managed with any of the following treatments:
- Spinal cord stimulators
- Pain medications
- Corticosteroids
- Topical pain relievers
- Antidepressants
- Physical therapy
- Healthy behaviors, including eating and sleeping habits
- Support groups and cognitive behavioral therapy
Some chronic pain conditions go away on their own; others stay for years. Regardless, treating chronic pain that results from a car accident will require the help and guidance of a licensed physician for the duration of your symptoms.
Proving Chronic Pain in Court
Chronic pain changes a patient’s life forever, and treatment can be expensive. When your symptoms resulted from a car accident that wasn’t your fault, you deserve to be compensated for your extreme pain and suffering, as well as the medical bills you may incur for treatment.
However, because pain is subjective, insurance companies may use it against you in a legal battle. They may assert that you aren’t actually in pain just to avoid liability for your suffering.
At PARRIS Law Firm, we do not let this happen. Our attorneys specialize in fighting for victims of catastrophic personal injuries, including horrific pain conditions such as CRPS.
When you are experiencing chronic pain after a car accident, hiring a lawyer is the surefire way to protect your rights.
Call PARRIS Car Accident Attorneys
PARRIS Law Firm is home to some of the nation’s best trial attorneys. We have been fighting for victims of catastrophic car accidents since 1985. Since then, thousands of clients have seen their lives restored.
Do not wait until it’s too late. If you’ve suffered injuries from a car accident, call PARRIS Law Firm, and we’ll review your case for free. You won’t pay a cent in legal fees until we win.
Here are more articles related to the same topic

Navigating the aftermath of a car accident can be a challenging ordeal, particularly when it leads to job loss. But can you sue for a lost job? Yes. In California, the law allows you to pursue a personal injury claim for lost income and lost earning potential. This blog aims to shed light on this complex issue, guiding you through the process of claiming compensation for a job lost due to a car accident.
Understanding Personal Injury Claims in California
Personal injury law protects individuals who have been physically or mentally injured because of the negligence or wrongful conduct of others. The purpose is to restore the injured party to their original condition by awarding them monetary compensation for their injuries and losses. In legal terms, these compensations are referred to as damages.
In car accidents, personal injury claims are exceptionally common. These claims can cover a range of damages, from medical bills and property damage to emotional distress and, pertinent to our discussion, lost income.
In California, the legal framework for personal injury claims is quite comprehensive. The State operates under a system of pure comparative negligence, meaning that even if you were partially at fault for the accident, you could still recover damages. However, your recovery would be reduced by your percentage of fault. For example, if you were found to be 20% at fault, your total recovery would be reduced by 20%.
To file a personal injury claim in California, the plaintiff (the person making the claim) must prove that the defendant (the person being sued) was negligent, and that their negligence caused the accident that led to the plaintiff’s injuries.
The four elements that must be established in a negligence claim are:
- Duty: The defendant had a legal duty to behave in a certain way towards the plaintiff.
- Breach: The defendant breached that duty by acting or failing to act in a certain way.
- Causation: The defendant’s actions (or inaction) caused the plaintiff’s injury.
- Damages: The plaintiff was harmed or injured as a result of the defendant’s actions.
If you’ve suffered job loss because of a car accident, it’s crucial to understand that lost wages fall under the umbrella of economic damages in a personal injury claim. Economic damages compensate the plaintiff for monetary losses, and unlike non-economic damages (like pain and suffering), there is no cap on the amount you can recover for economic damages in California, except in medical malpractice cases.
The process of claiming these damages is not a walk in the park. It requires substantial proof that your job loss was indeed a direct result of the injuries sustained in the car accident. This might involve medical records, expert testimonies, employer statements, and more.
The Connection Between Job Loss and Car Accidents
It’s not uncommon to assume that the fallout from a car accident is limited to physical injuries and damage to your vehicle. However, the repercussions can ripple into various aspects of your life, including your employment. Let’s explore how a car accident can lead to job loss.
Imagine this scenario. You’re a construction worker involved in a significant car accident that results in a debilitating back injury. The doctor advises several months of rest and rehabilitation, making it impossible for you to continue working in your physically demanding job. Your employer, unable to keep your position open indefinitely, is forced to let you go. Suddenly, you find yourself without a job, facing mounting medical bills and the loss of regular income.
In another instance, consider a professional violinist whose hand gets severely injured in a car accident. The damage to their hand means they can no longer play the violin, leading to an end of their career as a musician.
These examples illustrate the direct link between car accidents and job loss. But how does this translate into a personal injury claim?
Personal injury law in California allows you to recover economic damages–quantifiable monetary losses resulting from an injury. These damages are not limited to medical expenses and property damage but extend to lost wages and loss of earning capacity.
Lost wages refer to the income you would have earned had you been able to work during your recovery period. In our construction worker example, this would be the regular income lost during the months of rest and rehabilitation.
Loss of earning capacity is a bit more complex. It refers to the reduction in your ability to earn in the future because of your injuries. For our violinist, this would be the income they would have made from their career as a musician but are now unable to earn due to their hand injury.
It’s important to note that calculating these damages can be complex and often requires the testimony of economic experts. For lost wages, you would need to demonstrate your regular income before the incident versus after the incident. For loss of earning capacity, an expert might consider factors like your age, skill level, occupation, and the labor market to estimate the income you could have earned in the future.
Proving Your Claim: What You Need to Know About Lost Jobs Due to Car Accidents
The journey to compensation for a lost job due to a car accident is paved with evidence. It’s not merely about stating your case; it’s about proving it. But how do you go about this? Let’s break it down.
Personal injury claims revolve around the principle of negligence. You need to establish that the defendant was negligent and that their negligence caused the accident that led to your injuries and subsequent job loss.
To prove negligence, you’ll need to show that the defendant had a duty of care, they breached that duty, and that breach resulted in your injuries. Evidence can include traffic violation tickets, witness statements, police reports, and any other documentation that supports your claim.
Next, you need to connect your injuries to the accident. This is where medical records come into play. Doctor’s reports, X-rays, MRI scans, and any other relevant medical documentation can serve as concrete proof of the injuries you sustained from the accident.
So far, so good. But here’s where things get tricky—proving that your job loss directly resulted from the car accident. This requires a two-pronged approach. First, you need evidence that you were employed at the time of the accident, like pay stubs or an employment contract. Then, you need to demonstrate your inability to work is due to the injuries from the accident. This could be in the form of a doctor’s note recommending time off work or a statement from your employer that they let you go because of your inability to perform your duties.
If you can prove this, you’ll be eligible for economic damage. To claim these damages, you’ll need to prove your regular income and your potential future earnings. Pay stubs and employment contracts can help establish your regular income. For loss of earning capacity, you might need the testimony of an economic expert who can calculate your potential future earnings based on factors like your age, skills, occupation, and the labor market.
How PARRIS Law Firm Can Help
If you’ve lost your job due to a car accident, the path to recovery can feel like an uphill climb. You’re dealing with physical injuries, emotional distress, and now the loss of income. The legal process might seem like another complicated burden you don’t need. But that’s where PARRIS Law Firm steps in.
At PARRIS, we specialize in personal injury claims. We know the ins and outs of California’s legal landscape, and we understand the nuances of proving negligence, establishing damages, and securing compensation for our clients.
We have a proven track record of helping individuals who’ve lost their jobs because of car accidents. Our attorneys are not just knowledgeable; they’re persistent, dedicated, and committed to getting you what you deserve. They know how to gather evidence, construct a compelling case, and advocate for your rights in court.
At PARRIS, we believe in personalized service. We understand that every client, every accident, and every claim is unique. We take the time to understand your specific circumstances, your employment situation, and how the accident has impacted your life. We then tailor our approach to suit your needs, ensuring that we’re not just fighting for compensation, but for your peace of mind as well.
We’re here to guide you through the legal process, to help you understand your options, and most importantly, to fight for the compensation you deserve. We’re committed to ensuring that the law works for you, not against you.
If you’ve lost your job due to a car accident, get in touch with PARRIS Law Firm. Let us handle the legalities while you focus on your recovery. Because, getting you back on your feet is what matters to us. That’s not just our job; it’s our mission.

When you’re hunting for a personal injury lawyer, it’s about more than just checking boxes. It’s about understanding who’s going to be in your corner.
You’ll want to scrutinize their track record, discuss their fees, understand their communication style, and gain insight into their specific strategy for your case. Knowledge is power, and understanding their plan of action is non-negotiable.
Transparency is another major player in this game. Make sure they provide a clear breakdown of their fees and can walk you through the legal process without the jargon.
When looking for the right personal injury attorney for your case, there are many questions you should ask. Here are the top 13 questions to ask a personal injury attorney before you hire one.
1. How many years have you been practicing in California?
The number of years an attorney has been practicing and their area of specialization are important factors to consider when hiring a personal injury lawyer. This question gauges the depth of the attorney’s experience and their familiarity with the local legal landscape.
2. Have you always practiced personal injury?
An attorney who has been practicing for many years in California would have a comprehensive understanding of the state’s personal injury laws, court procedures, and legal community, which can significantly impact your case. If they’ve always focused on personal injury law, it indicates a dedication to this field, suggesting they possess specialized knowledge and skills, which could benefit your situation.
3. Can you provide examples of similar cases you’ve handled and their outcomes?
An attorney’s past performance is a reliable sign of their future competence. By asking this question, you can assess whether they have a proven track record in managing cases akin to yours. It offers a glimpse into their strategic approach, their negotiation skills, and their ability to secure favorable outcomes.
While success in past cases is encouraging, it’s not a guarantee of future results. Each case has its unique set of circumstances. However, an attorney who has consistently achieved positive outcomes in similar cases is likely better equipped to navigate the complexities of your case effectively.
4. What percentage of your cases settle out of court versus going to trial?
Most personal injury cases are settled before they reach the courtroom. This can be advantageous for the client, as settlements often mean less stress, lower costs, and quicker resolutions. However, the willingness and ability to take a case to trial if necessary is equally important. It demonstrates the lawyer’s commitment to securing the best possible outcome for their client.
The answer to this question can provide insight into the lawyer’s approach and strategy. An attorney who mostly settles might excel at negotiation, while one who frequently goes to trial is not afraid to stand up in court and push for a better result.
5. How often will we communicate, and who will be my point of contact?
This question allows you to understand the attorney’s communication style and frequency. Regular updates are not just about staying informed; they also provide reassurance that your case is being actively managed. You’re not just another file in a stack but a person whose life has been impacted by an injury.
Knowing who your point of contact is can eliminate potential confusion. Will you be speaking directly with the attorney, or will a paralegal or assistant handle most communications? A dedicated contact person ensures a smoother flow of information.
6. What is your approach to handling personal injury cases like mine?
Personal injury cases are not one-size-fits-all. Each case comes with its unique set of circumstances, requiring a tailored strategy. By posing this question, you get into the attorney’s thought process. You can gauge whether they take a meticulous, proactive approach or if they prefer to react as events unfold.
Are they aggressive, pushing for maximum compensation, or do they lean towards quick settlements to avoid protracted legal battles?
7. Can you walk me through the legal process I should expect?
This question allows you to gauge the attorney’s ability to clearly and concisely explain complex legal procedures. It’s paramount that you understand the road ahead. You need to know what steps will be taken, from filing the lawsuit to negotiation, settlement discussions, or even trial.
Their response will provide insight into their experience. An attorney well-versed in personal injury law should be able to outline the process with relative ease, demonstrating confidence in an otherwise daunting journey.
8. What is your fee structure, and are there any additional costs I should anticipate?
This question cuts straight to the chase. It clarifies what you’ll be paying for the attorney’s services and when you’ll be expected to pay. Most personal injury attorneys operate on a contingency basis, meaning they get paid only if you win your case. However, the percentage they take can vary, so get this clarified upfront.
Don’t forget about potential additional costs either. These could include court fees, expert witness fees, administrative costs, and more. While your attorney cannot predict an exact figure, a ballpark estimate can help you manage your expectations.
9. How long do you estimate it will take to resolve my case?
This question serves multiple purposes. First, it allows you to plan your life accordingly. Legal proceedings can be long-winded and disruptive. Having a rough timeline helps in managing expectations and mitigating stress.
Second, the response to this question reveals much about the attorney’s experience. Seasoned attorneys, familiar with the complexities of personal injury law, can provide a reasonable estimation based on their past cases.
However, remember that the law is not an exact science. Each case is unique with its own set of variables. An estimated timeline is just that—an estimate.
10. How do you determine whether to accept a settlement or go to trial?
This question probes the attorney’s decision-making process. It evaluates their ability to make calculated moves, balancing risks and rewards. A good attorney knows when to negotiate a settlement and when to fight it out in court.
But it’s not just about their decision-making ability; it’s about your involvement in that decision. A reputable attorney will include you in this process, considering your comfort level, financial situation, and long-term goals. They will also tell you when a settlement is in your best interest.
11. What potential challenges do you foresee with my case?
Asking this question will provide you with a roadmap of potential obstacles in your case. It’s about identifying the bumps before hitting the road. The response will offer a glimpse into the attorney’s analytical skills and their ability to anticipate and prepare for challenges.
But this is not just about hearing the challenges; it’s about understanding them. A competent attorney will not only list the challenges but also explain them in a manner that makes sense to you, and explain with clarity how they plan to overcome them.
12. If we lose the case, will I be responsible for any legal expenses?
This question addresses the elephant in the room—the possibility of losing. It’s not a pleasant thought, but it’s a scenario you must prepare for. The answer to this question will clarify who shoulders the burden of legal expenses if the case doesn’t swing in your favor.
It’s not just about knowing who pays; it’s about understanding how much they pay. An experienced attorney will explain the potential costs involved, giving you a clear picture of your financial obligations to pay them back for any costs.
13. Why should I choose you as my personal injury attorney?
This question allows you to assess the attorney’s confidence in their skills and their ability to articulate why they stand out from the crowd. You’re not looking for arrogance, but assurance that they possess the knowledge, experience, and dedication necessary to handle your case effectively.
A capable attorney will provide concrete examples of past successes, strategies they employ, and their unique approach to personal injury law.
PARRIS Law Firm Welcomes Your Questions
Each of these questions is a starting point for a broader conversation with potential lawyers. Ultimately, if you don’t feel comfortable with one, move on. This person will be your advocate, and you need to trust them.
PARRIS Law Firm has focused on California personal injury cases since 1985, securing billions in settlements and verdicts for our clients. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you.

When you’ve been injured, the path to recovery can be daunting. Legal complexities add another layer of stress to an already difficult situation. If you’re in California and find yourself in such a predicament, hiring a personal injury attorney could be your best decision yet.
Understanding Personal Injury Cases
Personal injury cases come in many forms, all hinging on the premise that a person has suffered harm due to another’s negligence or intentional misconduct. If you’ve been injured physically, emotionally, or financially because of someone else’s actions, you may have a personal injury case.
In California, personal injury cases take all kinds of forms. They can range from auto accidents (which are notoriously common given our state’s high traffic volumes), to slip and fall incidents often resulting from poorly maintained properties. Workplace injuries are also prevalent, especially in industries involving manual labor. Medical malpractice, product liability, and dog bites are other common types of personal injury cases in California.
The Role & Benefits of a Personal Injury Attorney
When you’re facing the aftermath of a personal injury, it can feel like you’ve been thrown into a labyrinth of legal complexities. This is where a personal injury attorney comes in. But what exactly does a personal injury attorney do?
A personal injury attorney is a legal professional who provides representation to those who have been injured because of the negligence or wrongdoing of another party. They are experts in tort law, which includes civil wrongs and economic or non-economic damages to a person’s property, reputation, or rights.
Navigating the complex legal system is no simple task, especially when you’re dealing with the physical and emotional toll of an injury. A personal injury attorney steps in to guide you through this maze. They handle everything from filing the legal documents to negotiating with insurance companies on your behalf, allowing you to focus on your recovery.
Here are some key benefits of hiring a personal injury attorney:
- Knowledge of Personal Injury Law: This is their field of practice. They know the ins and outs of the legal procedures, documentation, and other requirements of your case. This experience can help you feel more comfortable with the process and know that you have a trusted advocate fighting for you.
- Negotiation Skills: Insurance companies often attempt to offer the lowest possible amount for a settlement. Your attorney will skillfully negotiate on your behalf, working diligently to try to get you a fair deal.
- Court Representation: Your attorney will represent you in court, advocating for your rights and fighting for your best interests, even all the way through trial if necessary.
- Peace of Mind: Having a professional handle your legal worries can give you peace of mind, allowing you to focus on your recovery.
- No Upfront Fees: Most personal injury attorneys work on a contingency basis, meaning they only get paid if they win your case. This ensures they will work hard fighting for you.
Each of these points underscores the immense value a personal injury attorney brings to your case. They guide you through the complex legal system, negotiate on your behalf, represent you in court, provide peace of mind, and work on a no-win, no-fee basis.
Common Misconceptions about Hiring an Attorney
There are several misconceptions concerning the hiring of personal injury lawyers. These myths can deter injured individuals from seeking the legal help they need and deserve. Let’s address some of these common misconceptions and set the record straight.
Misconception 1: Hiring an attorney is too expensive.
Fact: Most personal injury attorneys work on a contingency fee basis. This means they only get paid if they win something for you—either through settlement or trial. You won’t have to pay anything upfront, and their fees will come out of your settlement. Therefore, hiring an attorney doesn’t have to be a financial burden.
Misconception 2: I can handle my case on my own.
Fact: Personal injury law is complex and navigating it without professional help can be challenging. An experienced attorney knows how to build a strong case, negotiate with insurance companies, and represent you in court if necessary.
Misconception 3: Lawyers drag out cases to make more money.
Fact: It’s in the best interest of attorneys to resolve cases as efficiently as possible. Prolonging a case unnecessarily can damage an attorney’s reputation and client relationships. They strive to get you the compensation you deserve in a timely manner.
Misconception 4: All personal injury cases go to trial.
Fact: The vast majority of personal injury cases settle out of court. Your attorney will work to negotiate a fair settlement with the opposing party. Only if a satisfactory agreement can’t be reached, will the case go to trial.
These misconceptions can prevent you from getting the legal help you need. It’s important to base your decisions on facts, not myths. A personal injury attorney is a valuable ally in your fight for justice and compensation. The PARRIS Law Firm is here to provide the support and guidance you need during this challenging time.
Costs Associated with Hiring a Personal Injury Attorney
One of the primary concerns when considering hiring a personal injury attorney is the cost. Many people fear that legal representation will be too expensive for them to afford. However, it’s important to understand the costs associated with hiring a personal injury attorney and why these costs are justified.
Contingency Fees: Most personal injury attorneys work on a contingency fee basis. This means they only charge a fee if they win or settle your case. The fee is typically a percentage of the settlement or award up to 40%. This arrangement ensures that you don’t have to pay anything upfront in exchange for the risks that the attorney takes putting their time and costs into your case. It also means you and the attorney share the same goal: to maximize your recovery.
Court Costs and Other Expenses: Besides the contingency fee, there can be other costs related to your case. These may include filing fees, costs for obtaining medical records, expert witness fees, and other court-related expenses. It’s important to note that these costs are often advanced by the attorney and later deducted from the final settlement or award.
Now, let’s address why these fees and costs are justified.
Experience: Personal injury attorneys bring their extensive knowledge and experience to your case. They understand the intricacies of the law, how to negotiate with insurance companies, and how to present your case in the best possible light.
Time and Effort: Building a strong personal injury case takes time and effort. Your attorney will spend countless hours researching, gathering evidence, consulting with experts, drafting documents, and negotiating on your behalf.
Risk Mitigation: By working on a contingency basis, your attorney assumes a risk. If they don’t win your case, they don’t get paid. This arrangement aligns your attorney’s interests with yours, ensuring they are incentivized to fight for the best possible outcome.
How to Choose the Right Personal Injury Attorney
Choosing the right personal injury attorney is a crucial step in your journey towards justice and compensation. But how do you know which attorney is the right fit for you? Here’s a guide on what to look for and some key questions to ask when interviewing potential attorneys.
Experience in Personal Injury: Look for an attorney who practices in personal injury law and has a proven track record of successful cases. While a history of success is not a guarantee they’ll win your case, a proven track record shows their dedication to their clients and the case.
Reputation: Consider their reputation in the legal community. Check online reviews, ask for references, and find out about their standing among peers and clients.
Communication: Your attorney and their team should be someone with whom you feel comfortable communicating. They should be able to explain complex legal terms in a manner that you understand and keep you informed about the progress of your case.
Fees: Understand their fee structure. Ask if they work on a contingency basis (where they only get paid if they win your case) or if there are any other costs you should be aware of.
When interviewing potential attorneys, here are some important questions to ask:
- What is your experience with personal injury cases similar to mine?
- How will you communicate with me throughout the case?
- Do you work on a contingency fee basis, and what does that mean for me?
- Are there any other costs I should anticipate?
- How long do you expect this case to take?
- If necessary, are you prepared to take my case to trial?
PARRIS Stands Ready to Help You
Hiring a personal injury attorney in California is not only worthwhile but often crucial for securing the justice and compensation you deserve. Choosing the right personal injury attorney can make all the difference. Look for experience, reputation, communication skills, and a clear fee structure. Ask questions and ensure they’re the right fit for you.
Now, it’s your turn to take action. If you or a loved one has been injured and you’re considering legal representation, don’t hesitate. Contact PARRIS Law Firm today. We’re here to stand by your side, fight for your rights, and help you navigate this challenging time. Your journey towards justice begins with a single step—make that step today.

A hit and run incident is a distressing event where a driver involved in a traffic collision flees the scene without stopping to identify themselves or assist the injured. These incidents often leave victims grappling with not only physical wounds but deep-seated emotional trauma as well. As a beacon of support during these trying times, PARRIS Law Firm brings its rich experience in championing the rights of hit and run victims, striving tirelessly to ensure justice is served and guiding victims on what to do after a hit and run.
Step 1: Ensure Safety
In the immediate aftermath of a hit and run incident, your personal safety should be your foremost concern. The shock and confusion that often follows such an event can be overwhelming, but it’s crucial to stay calm and composed. Your well-being is paramount.
If possible, move yourself and your vehicle out of the line of traffic. This minimizes the risk of further harm from oncoming vehicles and prevents additional accidents. However, remember to do this only if you can safely maneuver your vehicle. If not, leave it where it is and focus on getting yourself to safety.
Next, assess yourself for any injuries. Even if you feel fine, it’s essential to note that some injuries may not be immediately apparent due to the adrenaline rush following the incident. Therefore, always err on the side of caution. If you’re in pain or notice any physical discomfort, don’t dismiss it.
This initial step may seem basic, but it’s fundamentally important. In the chaos that typically ensues after a hit and run, prioritizing your safety creates a foundation for the subsequent steps you’ll need to take. It’s the first stride you take on the road to recovery and justice.
Step 2: Call the Police
Following a hit and run, it’s essential to report the incident to law enforcement as soon as possible. If you have an injury, California law requires you to report it to the police. This initiates the official record of the event, which will be crucial for insurance and potential legal proceedings down the line.
When you contact the police, be prepared to provide them with as much information as possible. This may include details about the other vehicle—such as its make, model, color, or license plate number if you were able to catch it. Also, describe the driver, the direction they fled, and any distinguishing features of the vehicle like decals or damage.
No detail is too small. The time of the incident, the location, the sequence of events, and even the weather conditions could all prove beneficial in the investigation. If there were witnesses, their accounts could also be invaluable.
By promptly reporting to the police and providing a detailed account, you’re not only fulfilling your legal obligations but also actively contributing to the pursuit of justice. It’s a critical step that could significantly aid in identifying the perpetrator and holding them accountable for their actions.
Step 3: Gather Evidence
After ensuring your safety and contacting the police, it’s crucial to gather as much evidence as possible from the scene. This step is pivotal in building a robust case, whether for insurance claims or potential legal proceedings.
Use your phone or camera to take pictures of the scene. Capture different angles and perspectives, focusing on the damage to your vehicle, any skid marks, broken glass, or other debris. These images can provide a visual account of the incident and help corroborate your story.
If there are any witnesses, politely ask them if they would be willing to provide their account of what happened. Their perspectives could be invaluable in painting a comprehensive picture of the incident. Make sure to note down their contact information for future reference.
Look around for any surveillance cameras that might have captured the incident. Businesses, traffic lights, or even residential homes may have security cameras that recorded valuable footage. While obtaining this footage may require some legal assistance, knowing its existence is a step in the right direction.
If you’re able, jot down your own account of the incident while it’s fresh in your mind. Include every detail you can remember, no matter how insignificant it may seem. As time passes, memories can fade or become distorted, so having a written record will be invaluable.
Step 4: Seek Medical Attention
Regardless of whether you feel injured after a hit and run, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately. The adrenaline that courses through your body in stressful situations can mask pain and injuries, causing symptoms to appear hours or even days later.
Visiting a healthcare professional ensures that any potential injuries are diagnosed and treated promptly. Conditions like whiplash, concussions, or internal injuries may not display immediate symptoms but could have serious long-term effects if left untreated.
Furthermore, seeking medical attention creates an official record of your injuries, which can be critical for insurance claims and legal proceedings. This documentation links your injuries directly to the hit and run incident, making it harder for insurance companies or defense attorneys to dispute their cause.
Don’t let the absence of apparent injuries lull you into a false sense of security. Prioritize your health; get checked out as soon as possible. This proactive approach not only safeguards your well-being but also strengthens your potential legal case. Your health is invaluable, and so too are the records that affirm its importance in the aftermath of a hit and run.
Step 5: Report the Incident to Your Insurance Company
Once you’ve ensured your safety, reported to the police, gathered evidence, and sought medical attention, the next crucial step is to report the incident to your insurance company. It’s recommended to do this as promptly as possible, as most insurance policies require immediate reporting of accidents.
When you contact your insurer, be prepared to provide them with a detailed account of the incident, similar to what you provided the police. This will typically include the time, place, circumstances of the incident, and any details about the hit and run driver or vehicle if available.
Share the police report number, the names and contact information of any witnesses, and photos or other evidence you’ve collected. Being thorough and proactive can expedite the claim process and ensure you receive fair compensation.
Dealing with insurance adjusters can sometimes be challenging. They are trained to minimize payouts, so they may question your account or downplay your injuries. Stay calm and stick to the facts. Do not speculate or guess about anything you’re unsure of. Remember, you also have the right to consult a lawyer before answering an adjuster’s questions, especially if you feel uncomfortable or pressured.
Step 6: Contact a Lawyer
The final step in navigating the aftermath of a hit and run is to consider seeking legal counsel. Dealing with the complexities of insurance claims and potential legal proceedings can be overwhelming, especially when you’re already coping with emotional distress and physical injuries. That’s where a lawyer comes into play.
A lawyer experienced in handling hit and run cases can help guide you through the labyrinth of legal and insurance procedures. They can ensure your rights are protected, deal with insurance adjusters on your behalf, and fight to get you the compensation you deserve. Their experience and compassion can significantly reduce your stress, allowing you to focus on your recovery.
Each step we’ve discussed—from ensuring your safety to gathering evidence, seeking medical attention, reporting the incident to your insurance company, and reaching out to a lawyer—is crucial in managing the aftermath of a hit and run. Each stage builds upon the last, creating a comprehensive approach to handle this unfortunate incident.
Having an experienced hit-and-run lawyer by your side can make a significant difference in your case. They bring a wealth of knowledge and resources to the table, providing you with the best possible representation and support during this challenging time. The road to recovery may be long, but with professional legal assistance, you won’t have to walk it alone.
You’re Not Alone: PARRIS Law Firm is Here to Help
In the aftermath of a hit and run, you may feel overwhelmed and unsure of what steps to take. Fortunately, you don’t have to navigate this challenging time alone. At PARRIS Law Firm, we’re committed to standing by your side and fighting for justice on your behalf.
With our extensive experience handling hit and run cases, our team has a proven track record of success. We’re dedicated to working toward our shared goal of getting you the compensation you need, while ensuring the process is as stress-free as possible.
If you or a loved one has been a victim of a hit and run, reach out to us today for a free consultation. Let us help you turn a traumatic incident into a path towards healing and justice. We’re here for you, every step of the way.

Parking lot accidents happen much more frequently than you might think. According to the National Safety Council, as many as 20% of all car accidents occur in parking lots and garages.
Why are parking lot accidents so commonplace? Some drivers let their guard down in parking lots and garages due to lower speed limits. In addition, distracted drivers make parking lot accidents more likely. Up to two-thirds of all drivers admit to using their cell phones while driving in a parking lot.
Despite what you might think, lower speeds do not guarantee pedestrian safety. Hundreds of innocent people are killed in the 50,000+ crashes that occur in parking lots each year. Thousands more are injured.
Given these parking lot accident statistics, it is crucial to know how to protect your rights in the event your car gets hit in a parking lot. If you or someone you love is hurt in a car accident in a California parking lot, the attorneys at PARRIS Law Firm can help.
Who is At Fault in a Parking Lot Accident?
Determining fault after a car accident is always tricky, and parking lot accidents are no exception.
The rules of the road apply in parking lots as they would on the street. Here are some of the most common parking lot accident scenarios, and who would be considered at fault in each:
Moving Cars vs. Parked Cars
- If a moving car hits a parked car, the moving car will always be at fault, so long as the parked car is legally parked.
- If a moving car strikes an illegally parked car in a parking lot, the moving car will still likely carry most of the fault, though insurers may assign partial fault to the illegally parked vehicle’s owner.
Two Moving Cars
- If one car stops and another car rear-ends them, the rear car will nearly always be at fault.
- If a car is making a left turn into a parking spot and hits another car going straight in their lane, the driver making the left turn will likely be at fault.
- If a car backs out of a spot and another car strikes them, fault will likely be assigned to the car backing out.
- If two cars back out of parking spots at the same time and hit each other, both drivers will generally be considered at fault.
- If two drivers turn into a parking spot at the same time, the driver turning right has the right-of-way. In the event of a collision, they may both share fault, or fault may primarily be allocated to the driver turning left.
Cars and Pedestrians
- If a car fails to stop at a stop sign or crosswalk and hits a pedestrian, the driver of the car will be at fault.
- If a car strikes a pedestrian walking outside a crosswalk, the driver will still generally be considered at fault. Pedestrians always have the right of way in parking lots.
- If a child runs behind a car that is backing out and the child is hit by the car, the driver of the car will likely be at fault.
What if the Parking Lot is Privately Owned?
Unlike roads and highways, many parking lots are owned by a company or private owner. When you go to a big box store, for example, the owner of the shopping center probably owns the garage, too. The owner of the lot is relevant because (a) it may play a role in who is at fault for your accident, and (b) it may influence police response to your accident.
Parking Lot Accidents and Premises Liability
Depending on the exact circumstances of your parking lot accident, the owner of the lot may be partially liable for your accident. For example, if the parking lot was poorly maintained or did not have proper signage regulating the speed limit, the owner may be liable for any crashes that occur on their property.
The property owner has opened up their parking lot for your visit. As a result, they must keep the parking lot safe by maintaining the roads, marking crosswalks, and erecting stop signs, among other duties. If they fail to provide “ordinary care” to the lot, and their negligence causes harm to a person on their property, they may be liable for any injuries they incur under premises liability law in California.
Private Parking Lots and Police Response
Police are required by law to respond to parking lot accidents if anyone is injured or killed, regardless of who owns the lot. However, if the accident did not cause any injuries and took place on a private lot, the police may or may not respond to 911 calls at the scene. If they do not arrive at the scene, you will not receive a firsthand police report to give to your insurance company.
Even without a police report, there are still steps you can take to protect your rights after a parking lot accident.
What to Do After a Parking Lot Accident
If a driver in a parking lot struck you or your car, there are steps you can take to protect your rights.
If your car was hit in a parking lot and the driver fled, you’ll want to call the police. Getting a police report will be extremely helpful for your insurance claim. You can also ask that the police request video footage from the property owner to try and locate the driver that hit your car. Being able to find out who caused the damage to your vehicle will help you collect additional compensation if your insurance company doesn’t cover your repairs or rejects your claim.
If you’re a pedestrian and you were hit by a driver, causing you injuries, you’ll want to take some additional steps beyond calling the police:
- Fleeing the scene of an accident (a hit and run) is a misdemeanor under California law, and a felony if anyone was injured. Even if you were not at fault, you should always stop to exchange information after a parking lot accident.
- Call 911. If anyone was killed or injured in the crash, calling the police at the accident scene is required by California law. Even for minor crashes, it can be useful to call the police to obtain a police report. As previously discussed, police may not respond to minor accidents in some privately owned parking lots. In these cases, it becomes even more crucial to gather information to support your claim down the line.
- Take pictures and videos. Sometimes, the best evidence of your parking lot accident will be pictures and videos you take immediately after. Make sure you get images of your injuries, every vehicle involved, and the entire parking lot area.
- Exchange contact information. You should swap information with the other driver whenever you’re involved in an accident. This includes names, phone numbers, addresses, driver’s license numbers, the VIN of both vehicles, and their insurance information.
- See your regular doctor. After your accident, visit your regular doctor as soon as possible. Injuries that may not present at the scene of the accident may crop up in the following weeks and months. Getting the medical attention you need as soon as possible is the best way to protect your rights in the event of a personal injury claim later on.
- Keep a personal injury journal. When you’ve been injured in a parking lot accident, it’s important to keep detailed records of how your injuries impact your life. Keep notes about how you’re feeling each day and what you were able to do (or not do) because of your injuries.
- Speak with a parking lot accident lawyer. Filing a lawsuit may be the furthest thing on your mind after a parking lot accident. But you may have unforeseen expenses related to your accident that your insurance won’t cover. You may need to file suit against the negligent driver and possibly the parking lot owner to get the full value of your claim. The right California parking lot accident attorney can help you.
How Do I Report a Parking Lot Accident?
Reporting a Parking Lot Accident to the Police
In California, you must report certain accidents to the police when:
- Anyone is injured or killed
- Property damage exceeds $1000
- Any of the drivers involved in the crash do not have a valid driver’s license
- Any of the drivers involved in the crash were under the influence of drugs or alcohol
- Any of the drivers flee the scene (hit and run)
If you call the police and they issue a police report, the police will file the report for you. If they don’t, you’ll need to do it yourself. You can do this by calling the nearest police station or California Highway Patrol (CHP). Once filed, you can get a copy of the report to give to your insurance company.
If you’re involved in a parking lot crash where the police won’t issue a police report because the parking lot is on private property, you can call the nearest police station and file the report yourself. California law requires you to do this if the driver who hit your car didn’t stop or leave a note.
Reporting a Parking Lot Accident to the DMV
You must also report your accident to the California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV). If local police or CHP took an accident report, you could use that report to file online with the DMV. You have ten days from the date of the parking lot accident to report your crash to the DMV. Failing to report an accident to the DMV could result in a driver’s license suspension, fines, and jail time.
Reporting a Parking Lot Accident to Your Insurance Company
Even if you’re not at fault, you’ll also want to report your crash to your insurance company. In fact, most insurance companies require this, even when you’re not filing a claim.
If you are going to file a claim with your insurance company, the sooner you start this process, the faster you can get your car repaired and your medical bills covered.
As a reminder, California insurers are not allowed to raise your rates for an accident that is not your fault. Reporting your accident is always the best way to protect your rights after a crash.
Speak with a Parking Lot Accident Attorney: Call PARRIS
After a serious injury due to a parking lot accident, the accident attorneys at PARRIS Law Firm can fight for your rights. To find out your legal options, contact PARRIS today to speak with an experienced California car accident lawyer. You have rights, and we can help you protect them.


